[Page 3]
Color D video clip. Aortic valve flow: locate and maximise regurgitant jet location/direction if any. See Online Calculator here. Exclude aliasing secondary to valvular or sub-valvular stenosis.
Check integrity of the proximal interventricular septum by searching for any sign of converging and accelerating flow (Proximal Isovelocity Surface Area) a possible marker of interventricular septal defect in this location.
彩色多普勒动态图像, 主动脉瓣血流;放大图像,找到返流的射流位置/方向;室间隔基底段完整性
CD video clip. Mitral valve flow: locate and maximise regurgitant jet location / direction,if any. Exclude aliasing secondary to valve stenosis.
See Online Calculator here.
彩色多普勒动态图像. 二尖瓣血流;放大图像,找到返流的射流位置/方向
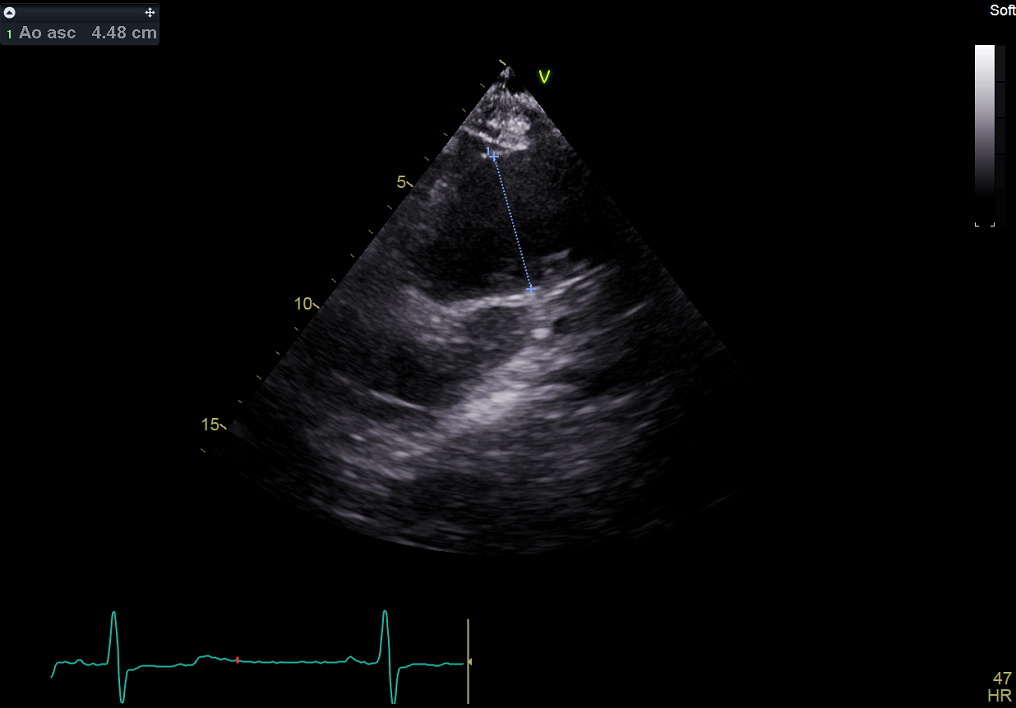
2d still frame. High left parasternal. Ascending aorta: measurement of anteroposterior diameter.
The ascending aorta – from ST junction upwards – is often better visualized by shifting (translating) the transduced 1-2 intercostal spaces upwards from the parasternal long axis view.
2D图像. 升主动脉; 测量:直径
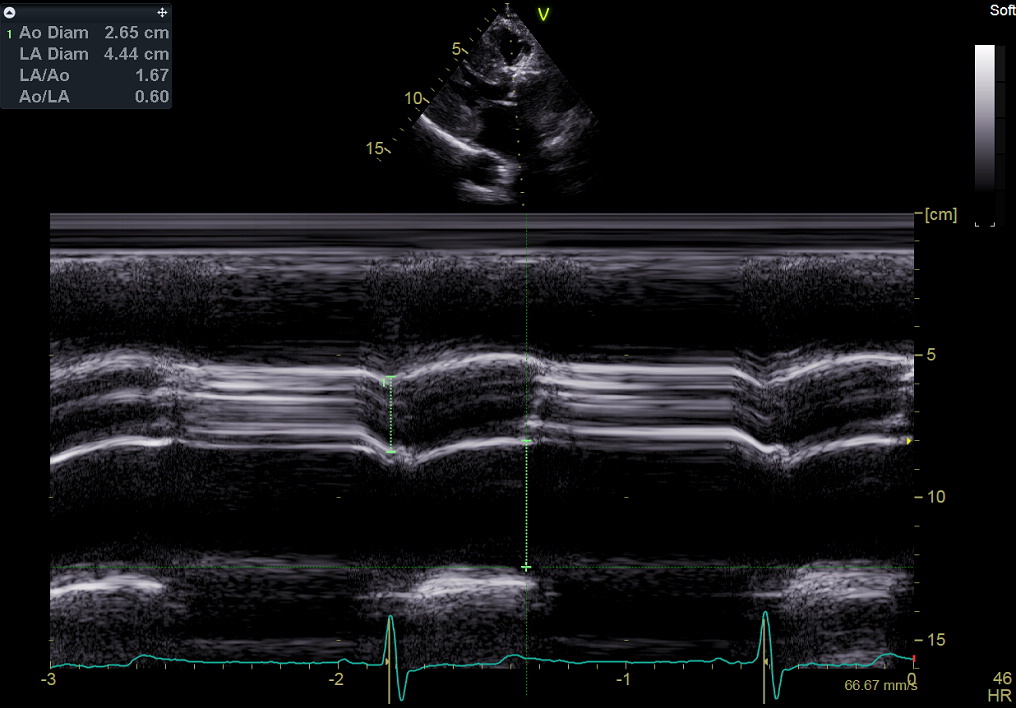
M-mode still frame. End-diastolic antero-posterior diameter of the aortic root; systolic separation of the aortic valve cusps; end-systolic diameter of the left atrium. See also here. Use the leading-edge to leading-edge method.
However, measurement of left atrial diameter is obsolete and should be substituted with the biplane volume (see Page 7), but may be useful when relating with colleagues from Electrophysiology or Cardiac Surgery: in these Departments, linear diameters are still used because of older population studies that used them.
M模图像. 主动脉根、主动脉瓣、左房

M-mode still frame. Mitral valve dynamics. Measurement of EPSS (early diastolic E-septal separation).
Note that 2D left ventricular linear measurements are preferable over M-mode measurements.
M模图像. 二尖瓣, 测量:EPSS