TT Mitral Prolapse
Mitral Valve Disease, end-systolic prolapse
February 28, 2021
(updated April 14th, 2022)
End-systolic Prolapse, Posterior Leaflet 收缩末期脱垂, 后叶
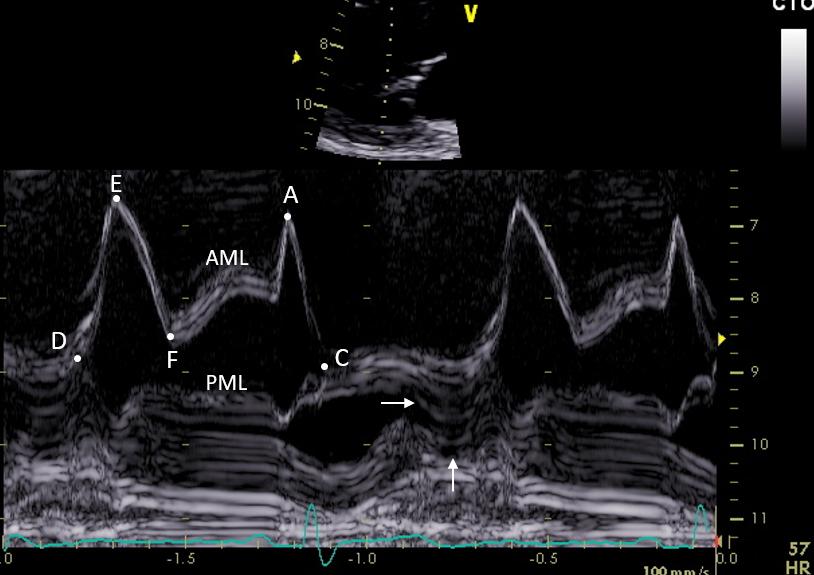
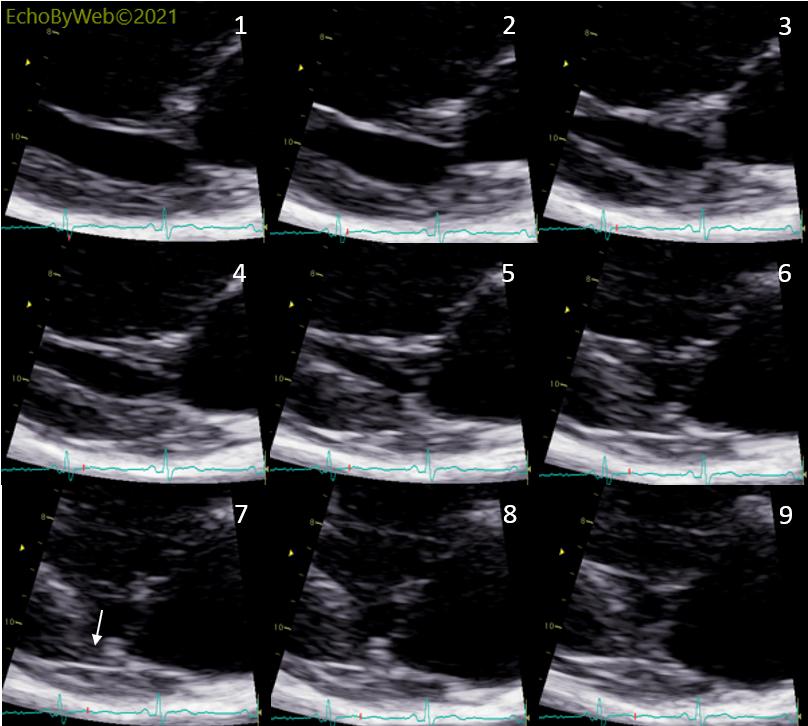
(tt4045) F, 56 y. 2D and M-mode imaging of a mild end-systolic prolapse of the PML. There is no significant regurgitation. Note the M-mode sign of the end-systolic prolapse of the PML (parallel lines bending posteriorly; horizontal arrow) and the hyperkinesis of the base of the LV posterior wall which on the M-mode tracing is seen as a large notch in the myocardium of the posterior wall (vertical arrow). The notch is caused by the hyperkinetic posterior wall moving out of the M-mode scanning beam (2D imaging, Fig. 1 and 2D sequential systolic frames in Fig. 3). Fig. 3 also shows that there is no MAD (mitral annulus dysjunction) in this case because the MV annulus is connected to the posterior LV myocardium (Fig. 3, frame #7, vertical arrow) throughout systole.
A: late diastolic opening (atrial systole) of AML; C: closure point of the MV; D: opening point of the MV; E: early diastolic opening (LV relaxation and fast LV filling); F: early diastolic closure (end of LV relaxation); AML:= anterior mitral leaflet; PML: posterior leaflet.
二尖瓣后叶收缩末期轻度脱垂的2D及M型图像。无明显返流。注意M型中收缩末期二尖瓣后叶脱垂信号(向后弯曲的平行线;水平箭头),以及左室后壁基底段运动过度,在M型图像轨迹中可见后壁心肌呈较大凹陷(竖直箭头)。这个凹陷的形成是由于后壁运动过度而移出了M型扫描声束的范围(图1,2D图像;图3,2D收缩期连续帧图)。图3也显示了此病例中没有MAD(二尖瓣环分离),因为二尖瓣环整个收缩期都连接于左室后壁心肌处(图3,#7帧, 竖直箭头)。
A: 舒张末期前叶打开 (心房收缩期); C: 二尖瓣闭合点; D: 二尖瓣开放点; E: 舒张早期打开 (左室松弛及快速左室充盈); F: 舒张早期关闭 (左室松弛结束); AML:二尖瓣前叶; PML: 二尖瓣后叶