[Page 9]
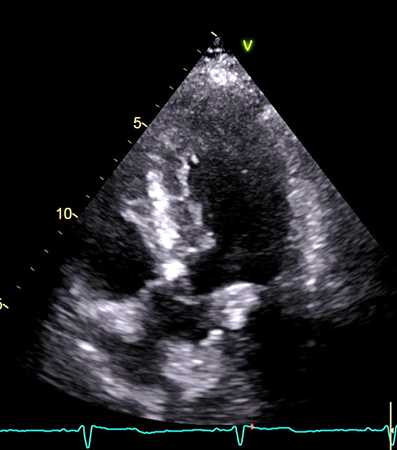
2D video clip. Apical 5-chamber view, obtained by tilting the transducer cranially until the aortic cusps are visualized. Anatomy and function of the aortic valve.
2D动态图像. 腔图,主动脉瓣
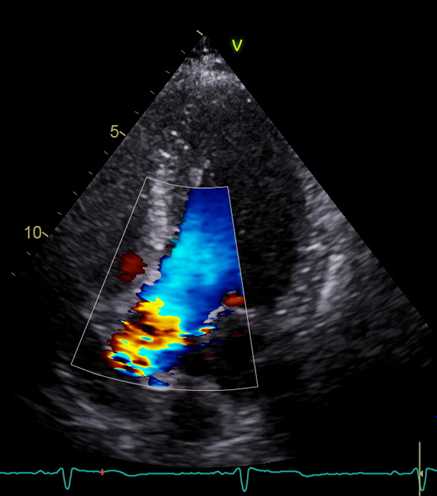
CD video clip. Apical 5-chamber view, aortic valve flow. Locate and maximise regurgitant jet location / direction, and evidence of valve stenosis (aliasing).
Identification of a Proximal Isovelocity Surface Area (PISA) if regurgitation is present.
彩色多普勒动态图像. 5腔图,主动脉瓣血流;放大图像,找到返流的射流位置/方向
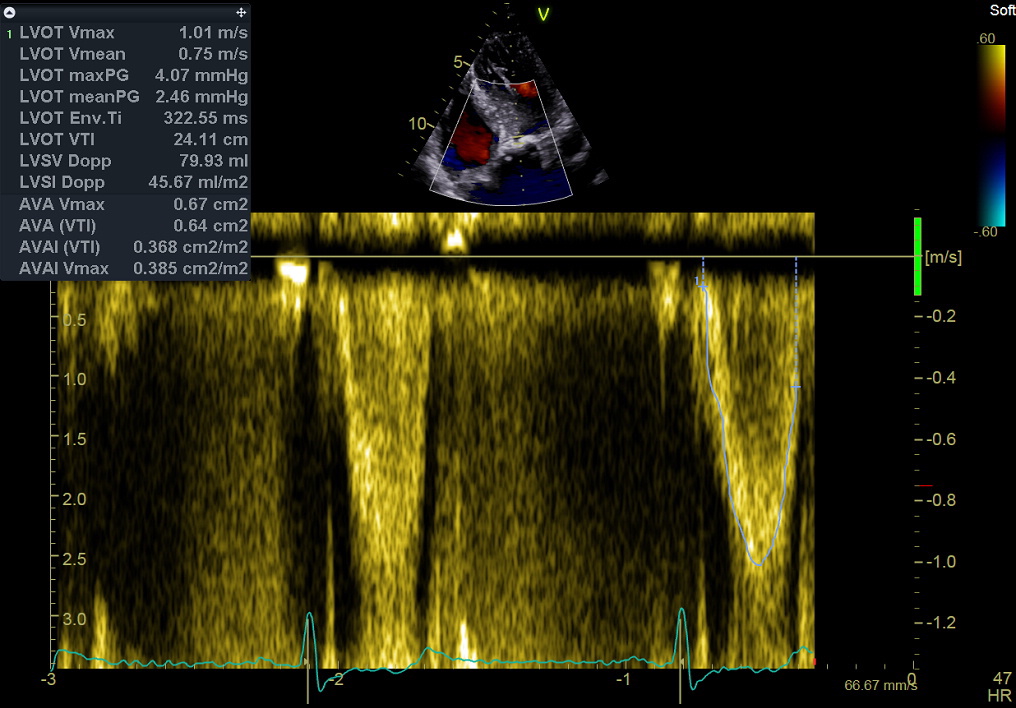
Pulsed Doppler still frame. Left ventricular outflow. Measurement of the outflow tract time-velocity integral, which is used by itself to “eyeball” left ventricular stroke volume, or together with the calculated area of the aortic annulus to calculate (forward) stroke volume (see Normal values here). See the Online Calculator here, and “How to calculate ventricular stroke volume using pulsed Doppler” in this website. Combined with mitral valve stroke volume, this measurement is used to estimate Regurgitant Volume and EROA of aortic or mitral regurgitation.
脉冲多普勒图像. 左室流出道血流;测量:左室流出道速度时间积分
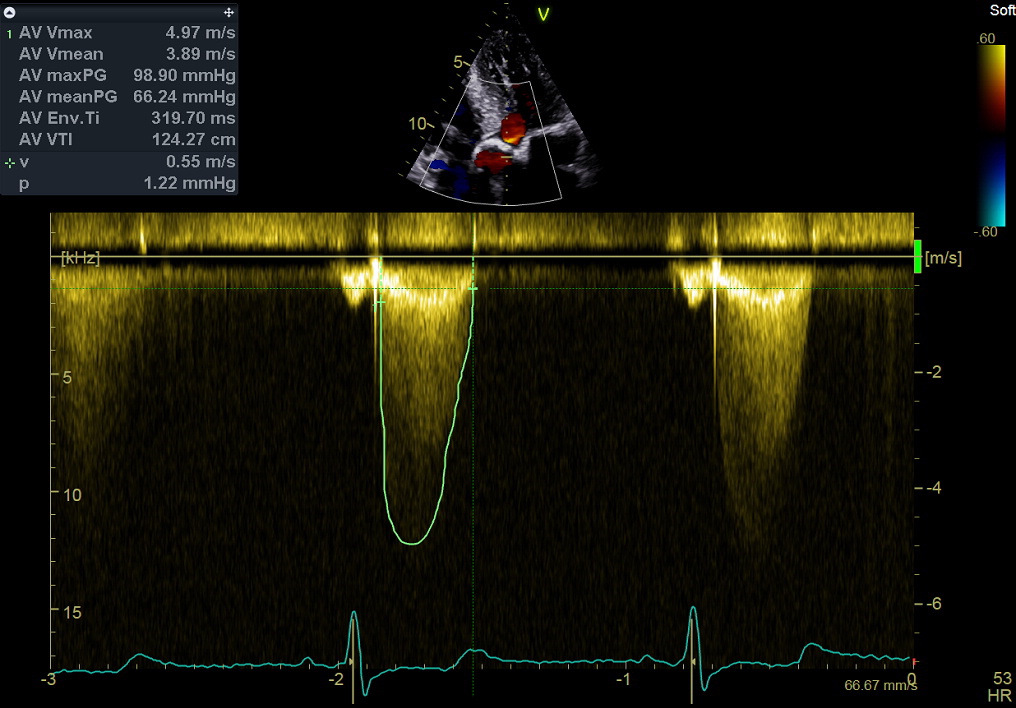
Continuous wave Doppler. Aortic valve flow. Measurement of peak systolic velocity and the time-velocity integral. These measurements are used in the evaluation of aortic valve stenosis. See the Online Calculator here.
连续波多普勒. 主动脉瓣血流;测量:速度时间积分