[Page 3]
Global longitudinal strain:
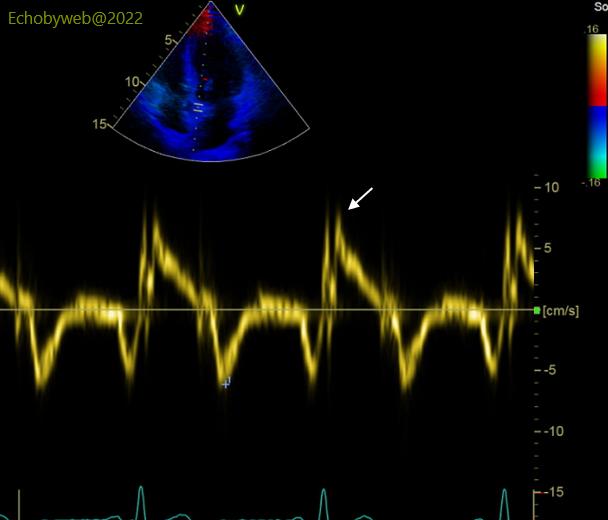
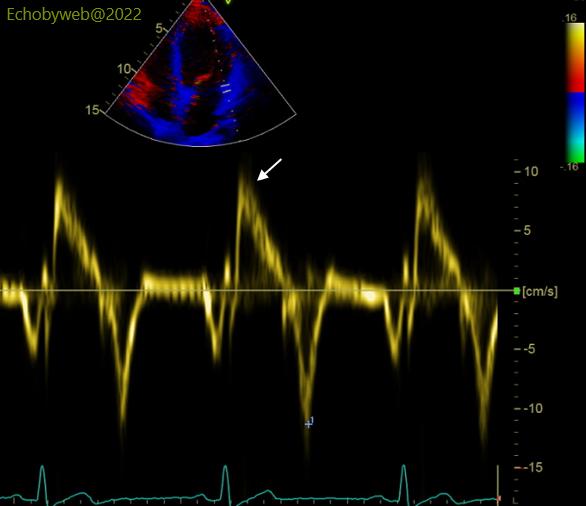
The pulsed tissue Doppler analysis of the mitral annulus shows a normal peak systolic velocity on both sides (Figures 9-10): 8-10 cm/s.
The Global Longitudinal Strain (GLS) – using GE AFI software – was normal (-19,9 %), with normal regional values for the 3 apical views (Figure 11).

However, at a closer look, LV segmental longitudinal strain values were abnormal in a rather large area which included basal and mid segments of the infero-posterior, lateral, anterior walls, and basal anterior septum (Figure 11). The colored arrows point at the corresponding peak systolic values of the said segmental curves. These segments are centered around the LAD perfusion territory (except the LV apex).
See the normal values for longitudinal segmental strain in this website, and compare the abnormal segmental values of this patient with the normal segmental longitudinal strain profile of the normal subject shown in Figure 12.
