[Page 2]
Left atrial pressure
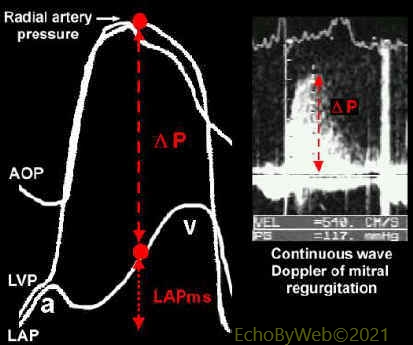
Figure 4. Left atrial pressure (mid-systole) = radial artery systolic pressure – maximum pressure gradient of mitral regurgitation.
LAPms= Systolic radial artery pressure (cuff) – DP = 125 – 117= 8 mmHg.
Radial artery pressure measured by sphygmomanometry (125 mmHg in the example).
DP: pressure gradient between peak aortic systolic pressure and mid-systolic left atrial pressure, which can be calculated (simplified Bernoulli equation, P= v2 x 4) from the peak velocity of mitral regurgitation;
a: left atrial peak a pressure
AOP: Aortic pressure
LAP: left atrial pressure;
LAPms: left atrial mid-systolic pressure;
LVP: left ventricular pressure
v: left atrial peak v pressure.
Right panel: transesophageal evaluation of mitral regurgitation.
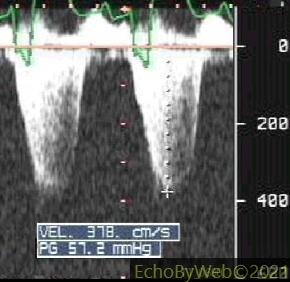
Figure 5. Transthoracic evaluation of mitral regurgitation associated with left ventricular systolic dysfunction (note reduced slope of velocity increase during isovolumic contraction), and elevated left atrial pressure.
Cuff radial pressure= 90 mmhg
LAPms= 90 – 57.2 = 32,8 mmHg.

Figure 6. Transthoracic evaluation of mitral regurgitation associated with mild reduction of left ventricular systolic function and increased left atrial pressure.
Cuff radial pressure= 100 mmHg
LAPms= 100 – 67.6 = 32,4 mmHg