[Page 2]
Aortic arch, 2D
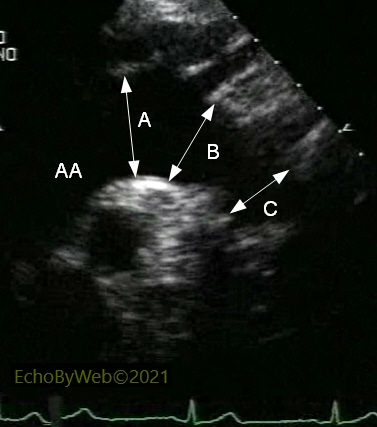
In 2D mode, with the transducer in the suprasternal notch, the long axis of the aortic arch is visualized with a 30°-45° leftwards (clockwise) rotation of the transducer. The anonymous, left carotid and left subclavian supra-aortic branches are often visualized. The proximal (A, just before the anonymous branch), intermediate (B, after the left carotid branch), and distal (C, just distal to the left subclavian branch) diameters of the aortic arch are measured between the superior and inferior inner borders (intima) of the aortic walls.
AA: distal thoracic ascending aorta.
Aortic arch, color Doppler
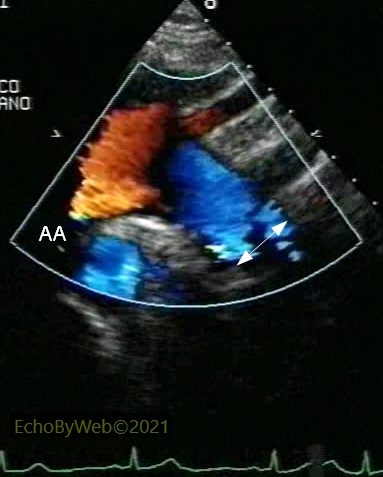
In color Doppler mode, the “pseudo-angiographic” effect of color Doppler flow (caution: gain should be lowered so that the color velocities do not “overflow” over the aortic wall tissue) may facilitate the measurement of the aortic arch diameters.
In the example (arrow), the measurement of the distal aortic arch is facilitated by addition of color Doppler imaging (compare to figure B above).
AA: distal thoracic ascending aorta.
Descending thoracic aorta, 2D
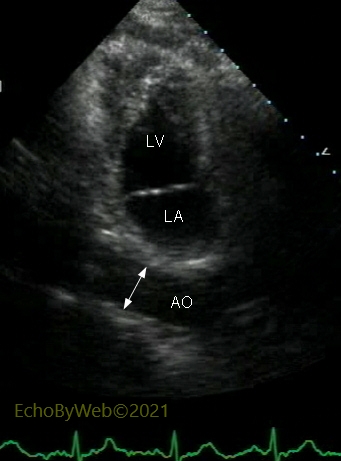
In 2D mode, apical modified 2-chamber view (transducer rotated to allineate with the long axis of the descending thoracic aorta), the diameter of the aorta is measured between the anterior and posterior inner borders (intima) of the aortic walls.
AO: descending thoracic aorta; LA: left atrium; LV: left ventricle.
Ascending aorta and arch atheromas
Montgomery’s Classification of Aortic Atheromas.
Class I. Normal or mild thickening of intima.
Class II. Extensive intimal thickening.
Class III. Atheroma < 5 mm.
Class IV. Atheroma > 5 mm. Class V. Mobile lesion.
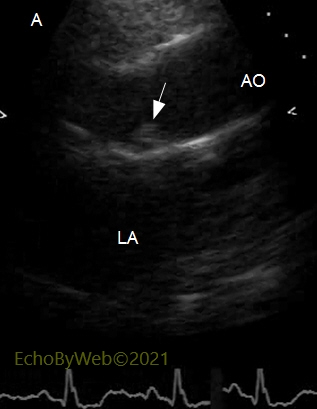
A. Class IV atheroma, ascending thoracic aorta.
2D mode, parasternal long axis view of the aortic root and ascending aorta.
The arrow points at an atheroma, located at the posterior sino-tubular junction, which protrudes more than 5 mm into the aortic lumen, and which is not mobile (Class 4).
AO: ascending aorta; LA: left atrium.
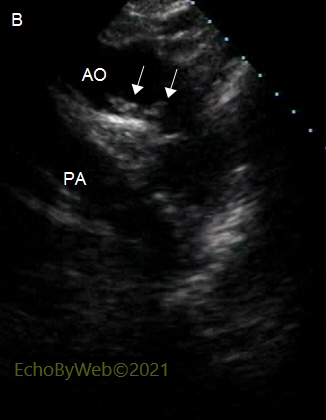
B. Class IV atheroma, aortic arch.
2D mode, jugular long axis view of the aortic arch.
Multiple atheromas (arrows) which protrude more than 5 mm into the aortic lumen from the inferior aortic wall, and which are not mobile.
AO: aortic arch; PA: left branch of the pulmonary artery.
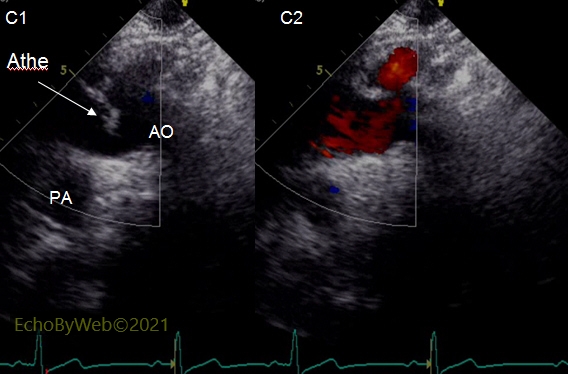
C. Class V atheroma of the aortic arch.
Color Doppler mode, long axis view of the aortic arch.
Large, mobile atheroma originating from the superior wall of the initial segment of the aortic arch (C1: diastolic frame; C2: systolic frame). In systole the atheroma “looks” into the brachio-cephalic branch.
AO: aortic arch; Athe: atheroma; PA: left branch of the pulmonary artery.